3DS
3DS is a security protocol used to authenticate users to protect card-not-present transaction scenarios against fraud, stymie unauthorized transactions, and reduce chargebacks.
Versions
- 3DS 1 Outdated - See roadmap below
- 3DS 2.1 Partially implemented
- 3DS 2.2 🌟 New
How it works
3DS Authentication flow
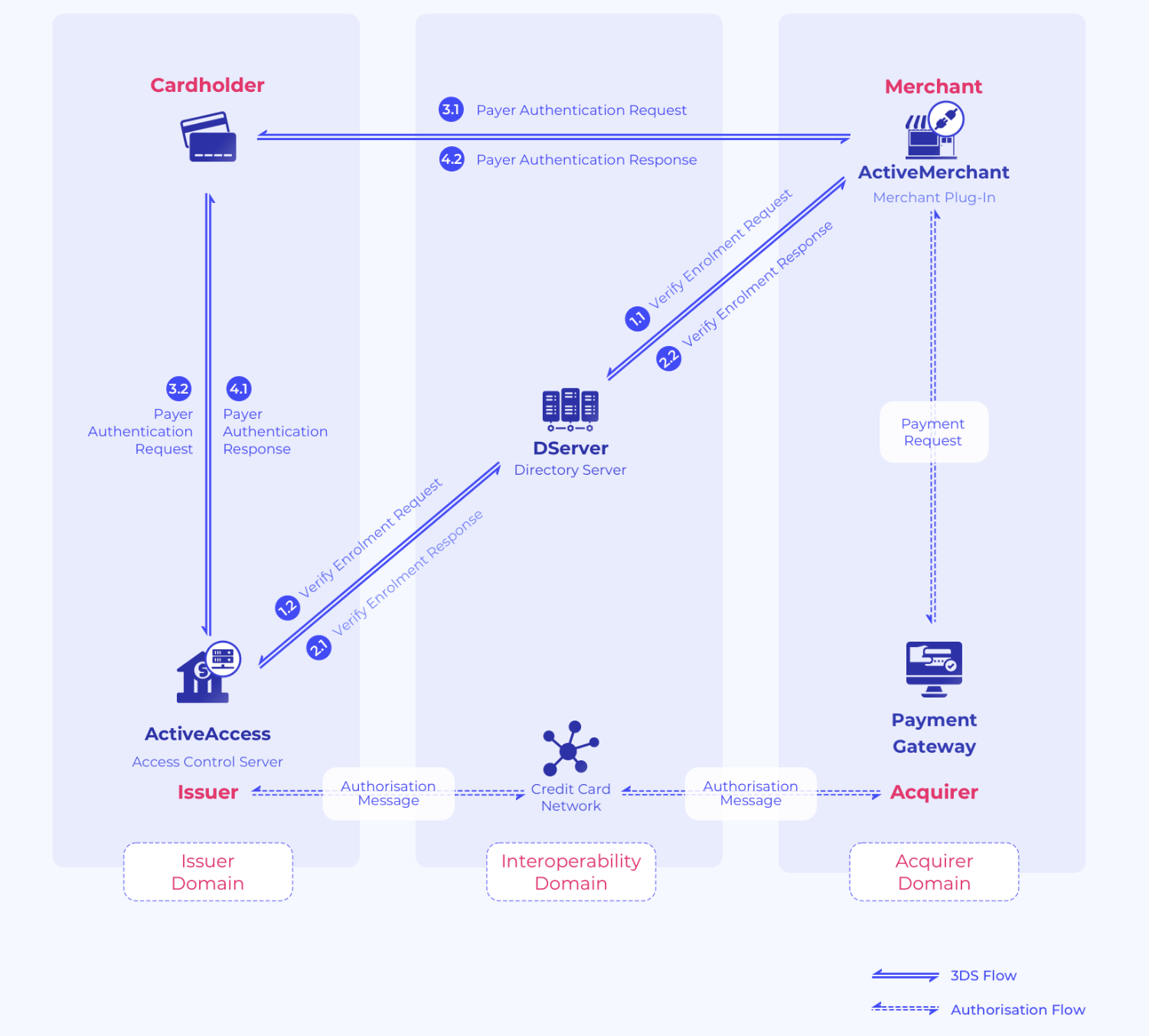 Source: gpaymentsopen in new window
Source: gpaymentsopen in new window
Differences
3DS1 vs 3DS2
3DS1 Features
- Support with dynamic linking
- Basic two-factor authentication
3DS2 features
- 3DS2 improves on 3DS1 with more data points that can be used to evaluate the risk level of a transaction
- Achieves Frictionless flow, that is,
- Better UX (User Experience) since 'trusted' parties don't have to authenticate each time
- Soft declines on transactions with context as to what business rule was not met an allowing the customer to reauthorize rather than restart the transaction
- Aligned to SCA therefore is more secure necessitating 2FA
3DS2.1 vs 3DS2.2
While both 3DS2.1 and 3DS2.2 support Frictionless flow, 3DS2.2:
- allows the merchant to request additional exemption through the Acquirer (Delegated Authentication)
- enables Decoupled Authentication where 2 different devices are used to complete the process
As Tutuka, we already partially supported 3DS2.1 for you to build on. Recently we've added a feature-set incorporating 3DS2.2. More about this in the release notes.
3DS1 and 3DS2 Roadmap
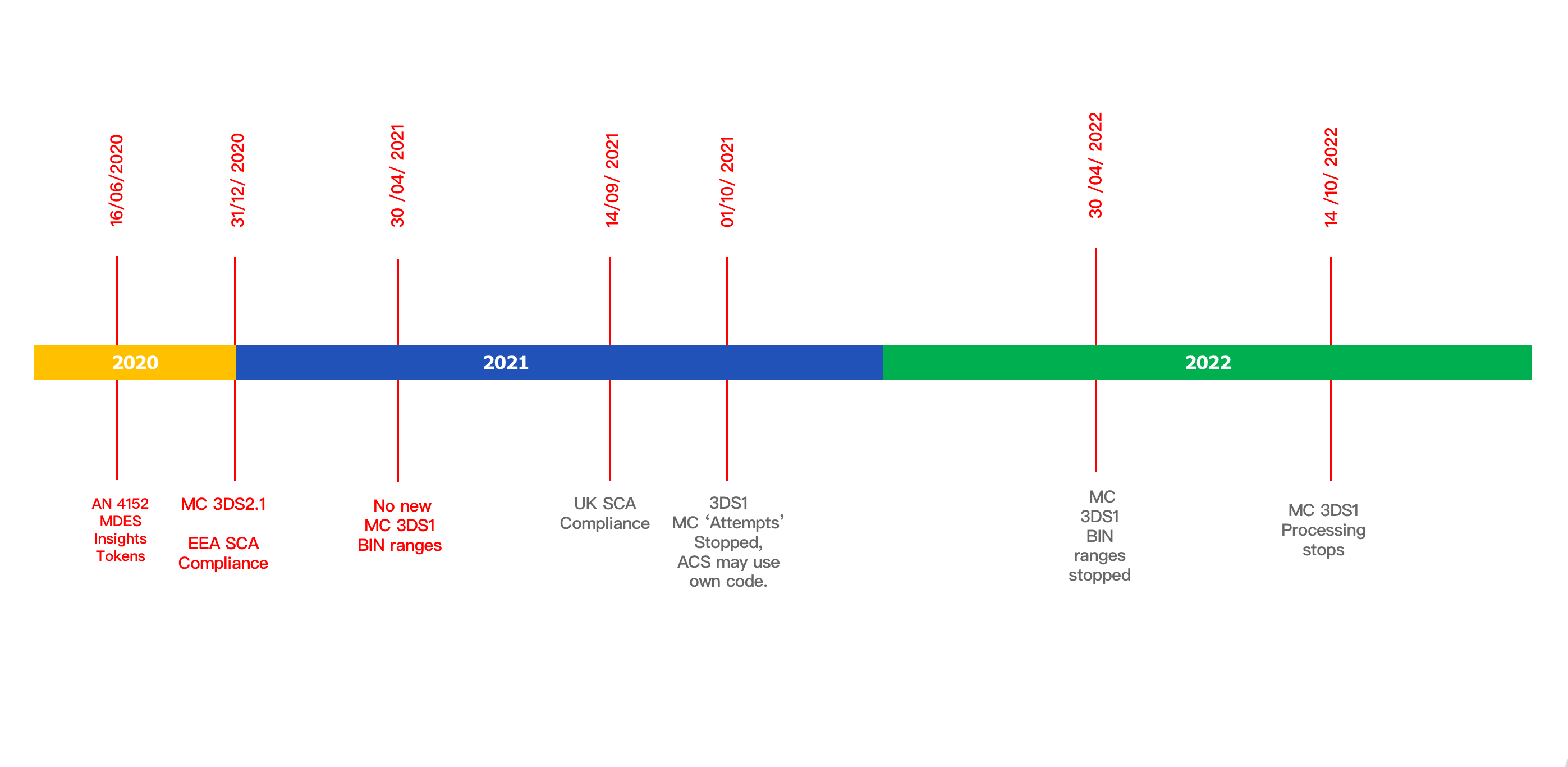
Key: (Consult our Glossary)
- MC (MasterCard)
- MDES (Mastercard Digital Enablement Service)
- BIN (Bank Identification Number)
- SCA (Strong Customer Authentication)
- ACS (Access Control Server)
